Xport-A functions as a chaperone by stabilizing the first 5 transmembrane domains of Rhodopsin-1
Por un escritor de hombre misterioso


Full article: The role of motor proteins in photoreceptor protein transport and visual function

EMC is required for biogenesis and membrane insertion of Xport-A, an essential chaperone of rhodopsin-1 and the TRP channel

EMC is required for biogenesis of Xport‐A, an essential chaperone of Rhodopsin‐1 and the TRP channel
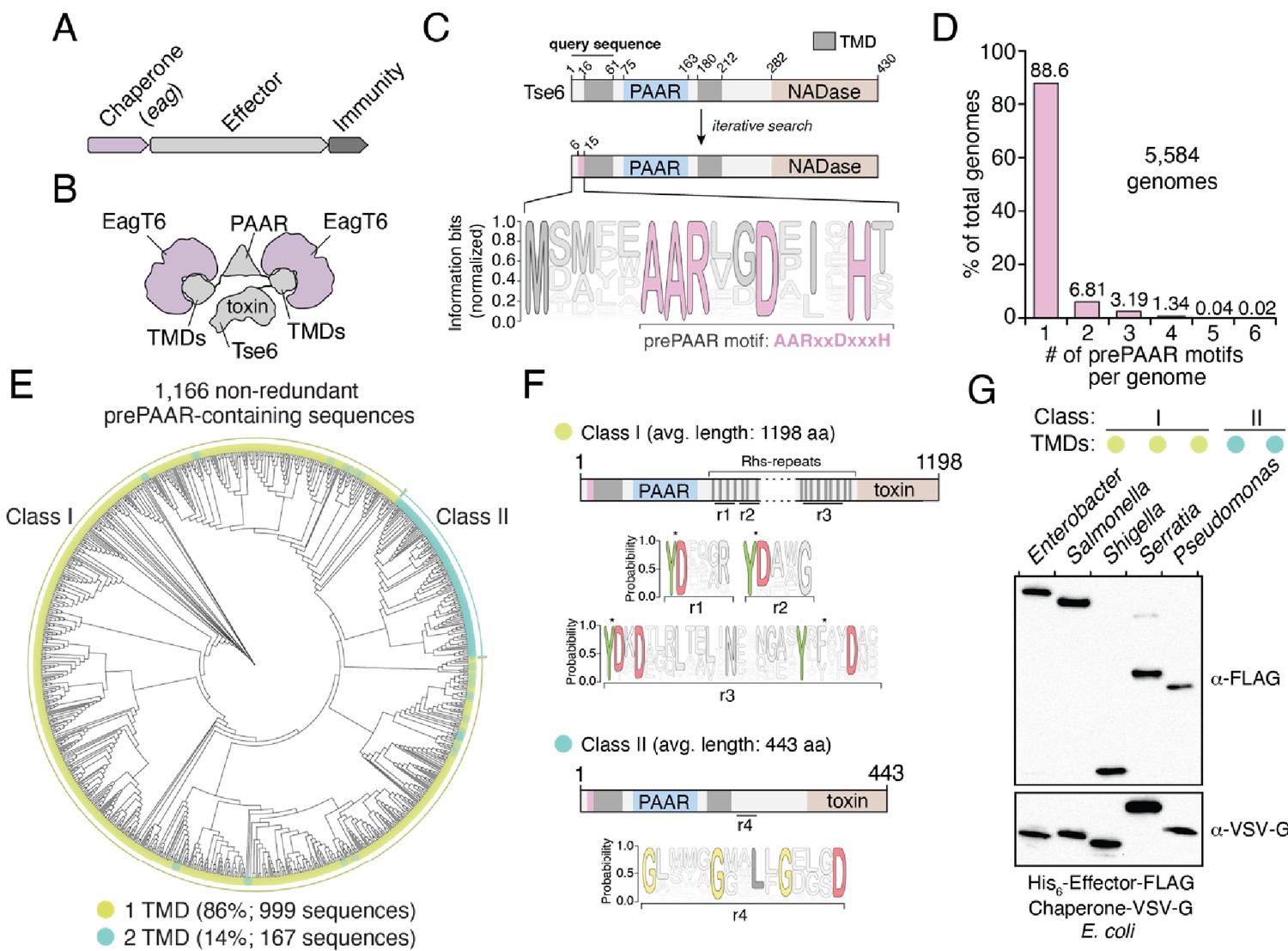
Structural basis for effector transmembrane domain recognition by type VI secretion system chaperones

Endoplasmic reticulum membrane complex (EMC) is not required for the

Dimeric Rhodopsin R135L Mutant-Transducin-like Complex Sheds Light on Retinitis Pigmentosa Misfunctions
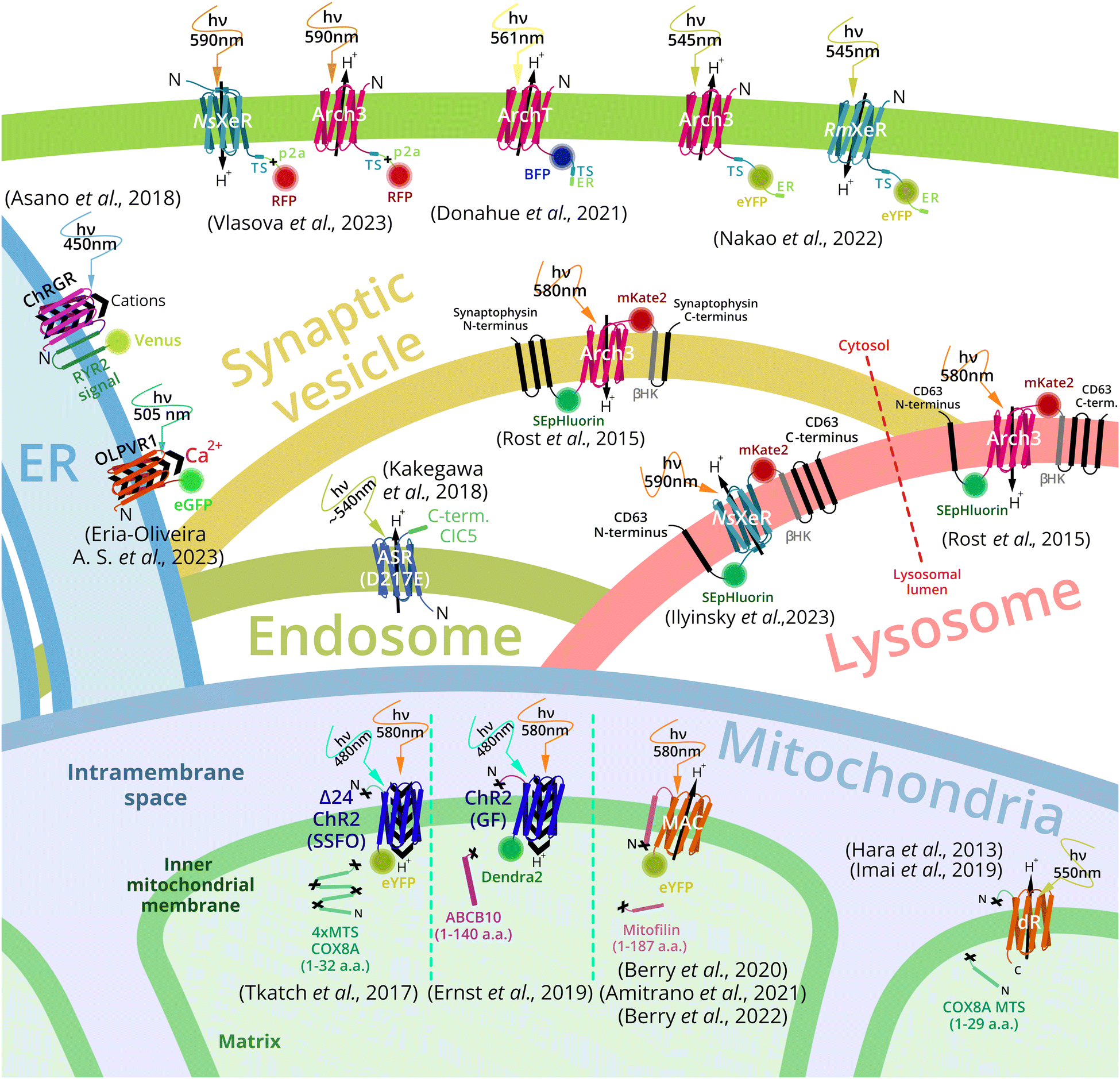
Intracellular microbial rhodopsin-based optogenetics to control metabolism and cell signaling - Chemical Society Reviews (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/D3CS00699A
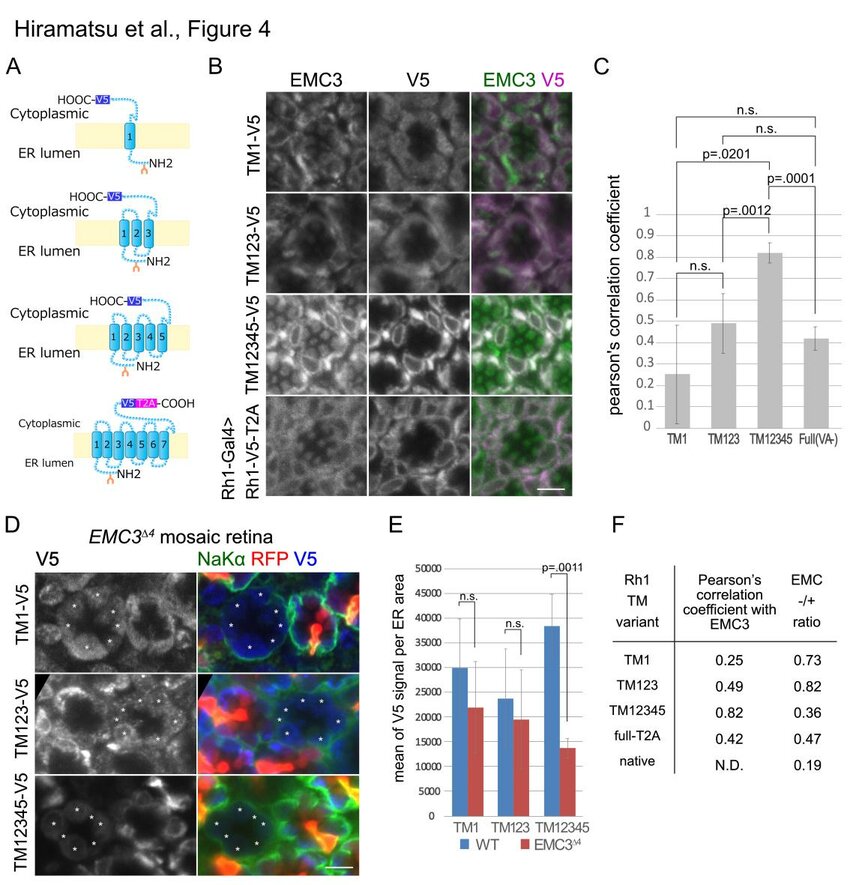
Endoplasmic reticulum membrane complex (EMC) may assist the exit of

Loss of hiro Accelerates the Course of Age-Related Retinal Degeneration

Chaperoning G protein-coupled receptors: from cell biology to therapeutics. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Advancing synthetic biology through cell-free protein synthesis - Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal
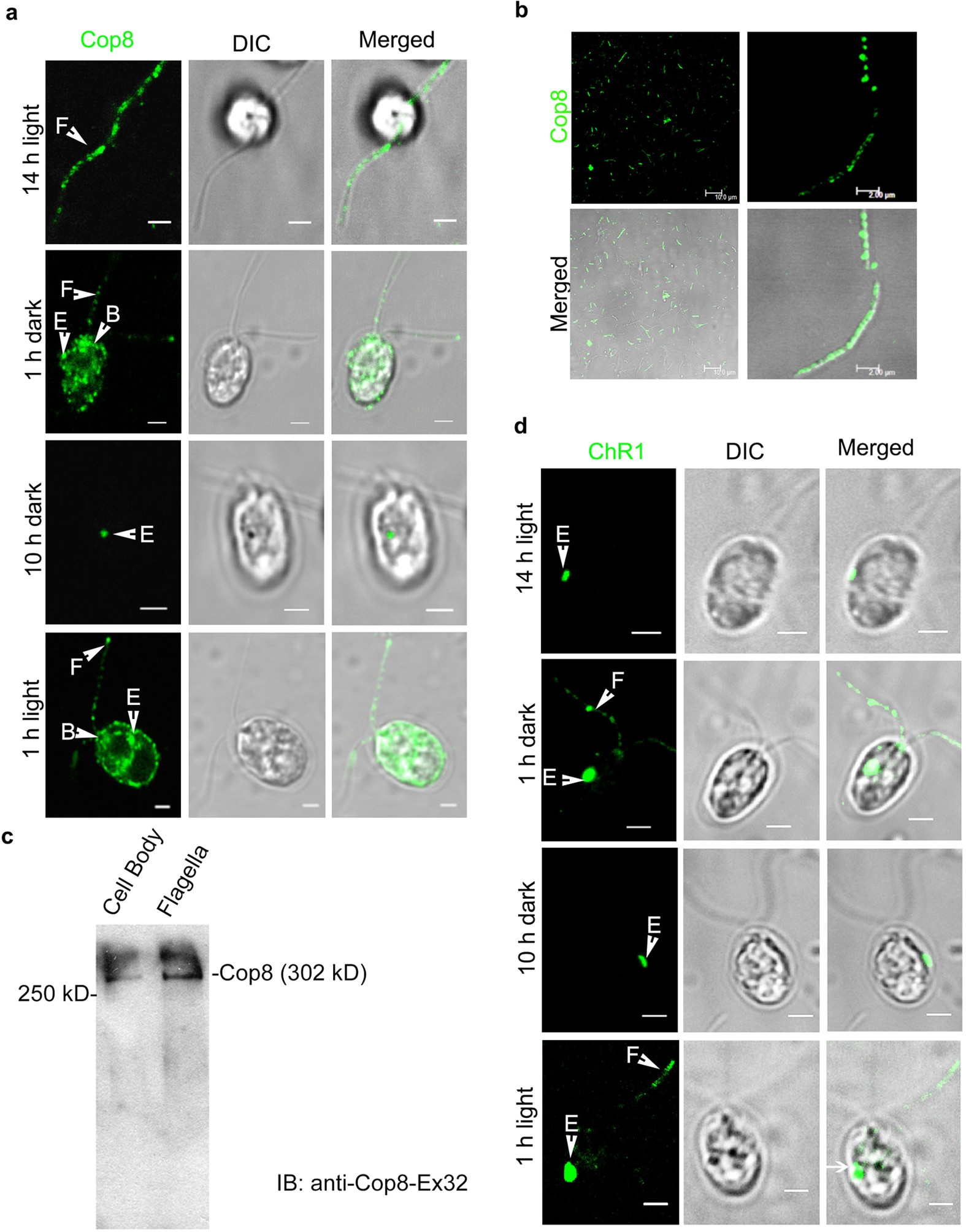
The trafficking of bacterial type rhodopsins into the Chlamydomonas eyespot and flagella is IFT mediated

The Role of EMC during Membrane Protein Biogenesis: Trends in Cell Biology

EMC is required for the biogenesis of Xport-A in mammalian cells. A

A model for EMC function in biogenesis of multi-pass membrane proteins.